New year, new chances, old problems. The perennial one of scheduling library time. I kind of started commenting on people’s posts and questions on FaceBook and then decided it merited a blog post on its own. There is also a whole discussion on libraries and librarians going at the IBO level where priorities, recognition, roles, responsibilities etc. are also being hashed out. But coming from a corporate background and not an educational one, I sometimes can’t help seeing things a bit differently.
One of the most useful courses I followed during my librarian studies was “Designing spaces for learning”. And spaces weren’t just physical spaces, or even physical and online spaces, it includes temporal space – as I wrote about here and design thinking. The thing is that time is the great leveller. We all have 24 hours of it a day, but what we choose to do with it is telling, because it will determine who we are as librarians and display our priorities more strongly than just about anything else we do. I could even put money on the fact that if you walked into a school where there was a troubling relationship between the librarian and staff / admin and you asked to see the library timetable it could be used as both a diagnostic tool and a cure.
So I’ll begin this post by giving a shout-out to my principal who gives me the autonomy necessary to both think all this out and then to discuss it with her and implement it. She also gives me the support I need when things are not working optimally, if I’m reasonable in my requests and it supports student learning. My PYP coordinators who are allowing me to be their educational partners also makes things a lot easier. And the school I’m at that generously allows for 3 support staff members in the library in their HR budget to open up time for me to be doing higher order teacher-librarian things rather than processing and circulating books. Now apologies for a barrage of management-type speak and jargon, please bear with me.
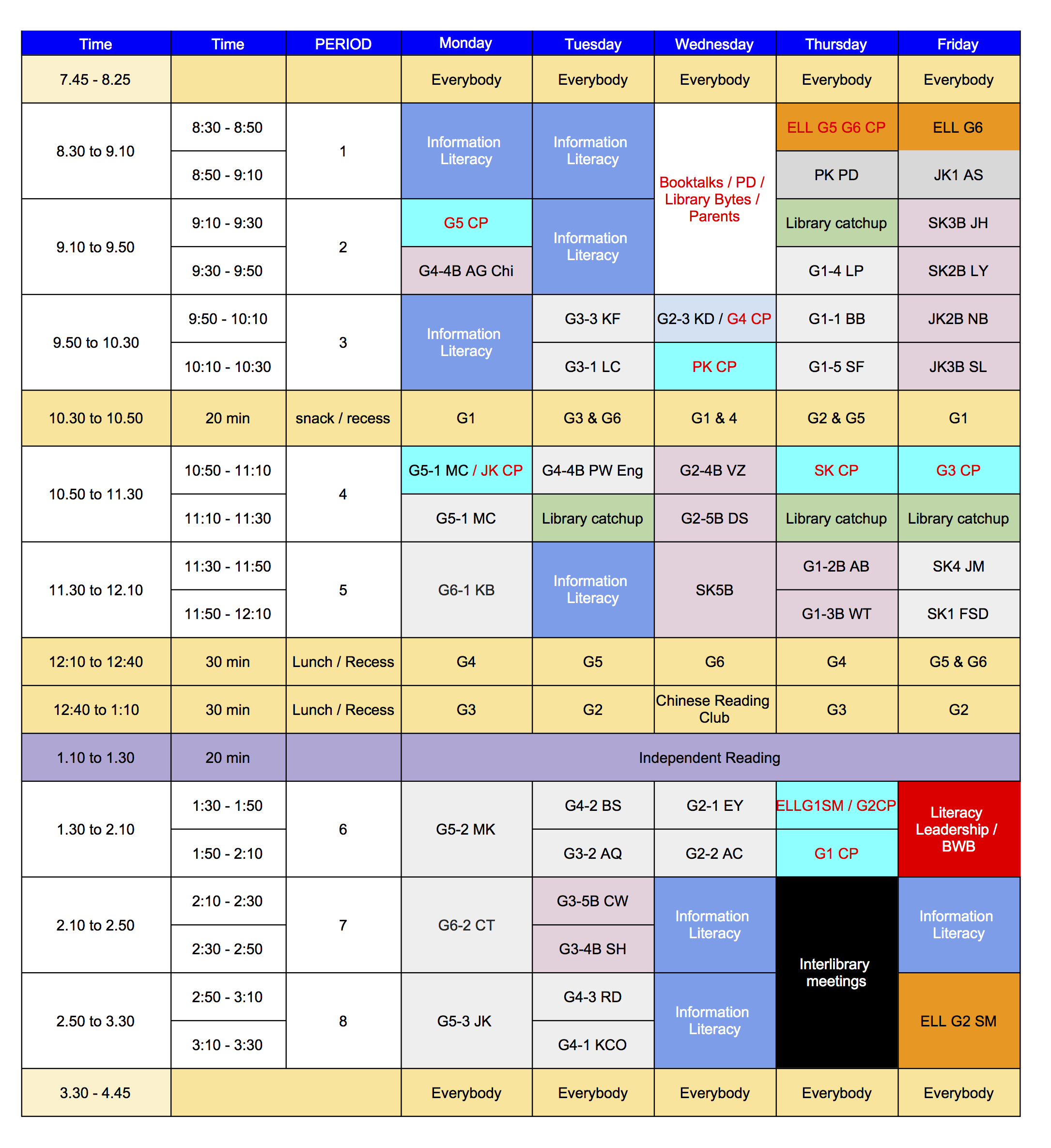
In library scheduling there are two main schools of thought, primarily defined as fixed scheduling (you set up a schedule each year / term, and every class gets their time to go to the library at that designated time) and flexible scheduling (the librarian’s time is bookable, on demand). Each have their benefits and drawbacks – with fixed you get to see everyone regularly, but in a large school you have no time left, or go on a two / three week schedule. With flexible you run the risk of never ever seeing some kids depending on the teacher’s ideas of the library, priorities etc. Most larger schools where the ratio of librarian to students is low (e.g. 1 librarian to 1500 students) opt for a flexible schedule. Our ratio is 1:630 with 34 classes so theoretically a fixed schedule can work, and I’ve tried to build some flex into it otherwise I’d never do the things that differentiate me from what a teacher or library assistant can do.
Priorities
The first part of the process is to decide what your priorities are. Now in education this is way harder than in corporate life, since often many of your priorities are set for you. It also took me a little while to get the experience and confidence to actually realise what my priorities should be and to advocate for them. And also to decide what my priorities shouldn’t be and to draw a line in the sand. Part of your priorities are governed by your school’s mission and value statement. Part is about your integrity to yourself as a professional (teacher) librarian and part is about the resources physical and financial your school has.
My personal priority statement is “I am about literacy“. So everything that has to do with any of the literacies (alphabetic, informational, numerical, multi-lingual and to a certain extent digital) I will prioritise. I steer clear of discussions on makerspaces for that reason, partly because we have a dedicated STEAM department, and partly because if it has nothing to do with creating some form of reading, writing or research I consider it outside of my ambit. OK, shoot me, but you have to draw the line somewhere or you’ll have to compromise on something else, or just never stop working 24 hours a day.
The next thing is to think about how you are going to integrate yourself into teaching and learning in a collaborative way. There are two frequent laments heard in this regard “I don’t have time for meetings” and “I don’t get invited to meetings” – and here is where a supportive principal comes in. The very first thing that went into my timetable this year were the days and times for co-planning for each grade. It’s taken 2 years to get to this point and I only need / want to go to the meetings once a unit – usually a week or so before the unit starts so I’m involved in hearing where the team wants to go with the unit, what digital and physical resources they need and how I can meaningfully integrate information literacy or other ATL skills into the unit. I also only need to be there for about 10-20 minutes depending on whether it’s an old or new unit. So what about the other 4/5 weeks? Well I’m using the time to DO what the team needs. And if I’m teaching in that time, I can’t be doing. Doing includes making library guides (that’s how I have time for them), curating resources, ordering new resources, weeding old resources. Although I am not considered a HOD, my principal also kindly invites me to the weekly lead meetings so I know what is going on and coming up, and can involve the library in any way that is meaningful.
Then comes the fixed part, which fulfils my literacy priority. Since I do have a manageable ratio / number of students / classes, I have a fixed part of my schedule whereby each student gets to come to the library once a week. How has this been engineered? By chunking time and students. 40 lesson periods and 34 classes would mean no time for co-planning, co-teaching, own planning let alone the library facility management stuff. So, based on the advice of my predecessor and in the face of intense resistance from teachers, the timetable was split into 20 minute library times from G4 and under and kept at 40 minute sessions for G5 & 6. The compromise for lower level teachers is they can pair up with another teacher in the same grade had have 40 minutes with 2 classes. It’s not my preference, but they may choose this. I do this because I want to see every single child every single week and make sure that I am helping them with free voluntary reading. In Krashen’s (2004) words ” evidence from several areas continues to show that those who do more recreational reading show better development in reading, writing, grammar and vocabulary, These results hold for first and second language acquisition, and for children and adults. ” I am an unabashed book pusher. I do everything I can to put books in the hands of children that they want to read. And to do that I need to see them and I need to know them. Especially the ones that will only come to the library that once a week.
Yes you can do a library lesson in 20 minutes, if you have staff who can do the check-in / check-out and shelving while you’re doing the reading, the mini-lesson and the reader-advisory, and if your teachers are in the library helping. Yes I do get that much support from my school and I’m very grateful for it.
Another small note on this section – switching costs nearly killed me in my first year. I was doing a G1 class then a G6 class then a G3 class then Kindergarten jumping around day in and day out. So I asked teachers to try and schedule in the library so that all the classes in a grade (or 2 grades, depending on number of classes) were on the same day. It worked last year and we kept it up this year – it was actually easier timetabling that way – constraints work. There were only 2 exceptions where the larger school timetable and teacher preps meant that I’m taking a class to help them out on a day different to the rest of the grade. That’s not bad going.
My next priority is multi-lingual literacy. Actually part of it comes in the fixed part. We are a bilingual English/Chinese school. I am the parent of two bilingual children. A child is NOT bilingual unless they are bi-literate. I will not compromise on that. I faced fierce opposition from parents complaining via teachers when I insisted that every child in the bilingual program had to take home a book in each of the languages irrespective of their ability to read in that language at that point*. I am very uncompromising on some things and this is one of them. At home, I have two bilingual teenagers, one in Chinese, one in Dutch who are still doing their languages as a first language only because I am uncompromising on the fact bilingual has to be bi-literate otherwise you are fooling yourself. And bi-literate means reading and writing. The classes that have “first dibs” on the library timetable are the bilingual teachers. One of my library assistants has to be fluent in Chinese and able to read aloud to my students and help me curate chinese resources.
So those are the bilingual classes. We also have ELL (English Language Learners) and students doing French as a second language. Their teachers also have (and take) the opportunity to bring their students into the library (or the library classroom where my world language resides) with their students every week. Language can just not be taught in isolation from books and reading.
The learning eco-system priority. Teaching and learning does not occur in a vacuum. Children are part of a family, a linguistic community, a social community, a cultural community. At the primary level, besides teachers, parents are my best allies in my literacy goals for my students. So they get two periods once a week for library information sessions, for time to drop in for some reader advisory, for meetings the school needs to hold in my space for them. I am a neutral zone. I am there to help them realise their goals for their family.
Then there is my co-teaching / information literacy teaching priority. I’m listing this last just because it’s last in the process, not because it’s last in priority. Doing all the above, specifically the 20 minute slots with the younger kids gives me 8 x 40 minute periods where I can make myself available for whatever lessons my teachers would like me to teach in the library or in the classroom. These are not used every week, but now that we’re integrated the research ATL into units they will be used far more.
My library facility priority, means I’ve blocked off 2 periods for inter-campus meetings, either by google-hangout or face2face with my fellow librarians and with my own staff.
These are my priorities and how I’ve structured my temporal space to accommodate them (see below). I’m in primary school – people in MS or HS may have other priorities and concerns. People in larger or smaller schools will have other issues. But the bottom line is your priorities need to be worked out (it’s taken me 2 years to get here and to articulate them), and reflected in your timetable. And you need to articulate them well so that if necessary you can argue your case with whoever is getting in the way of allowing you to reflect them in your timetable. Things may and probably will change, but that’s it for now.
As a closing note – another part of the IBO library/librarian discussion was about the “super-librarian” archetype. I don’t want to be a super librarian. I want to be a great librarian. When Clark Kent is busy being superman, he neglects being Clark Kent. We cannot afford to be super-librarians because super librarians can and do burn out. And while everyone around this type of librarian says how super-librarianish they are, I don’t think they get the recognition they really deserve as librarians. And their successors have big shoes to fill, but not necessarily the right shoes to fill.
* Why do I insist on this? Often they can’t read the book, sometimes/ often their parents can’t read the book. Because they can’t read the book YET. Just like my kindergarten and pre-kindergarten children take home books they can’t read, so too my English / French / Dutch speaking kids take home Chinese books because the assumption has to be that they WILL be able to read those books. Otherwise get out of the bilingual program. Seriously. What do we do with mono-lingual kids who can’t read? We read to them. What if we can’t read? We sit and page through the books with them and we ask them to explain the pictures to us. We ask them to point out the words they do recognise. We ask them to point out the letters they recognise.




 In my current position I’m considered to be part of the school wide coaching team, and as a group it was suggested we read “
In my current position I’m considered to be part of the school wide coaching team, and as a group it was suggested we read “ information structure
information structure





